What are you seeing?
Wi-Fi connection issues.
Why are you seeing it?
Wi-Fi performance and Wi-Fi connection issues may occur due to a number of reasons. Some examples of these include outdated or incorrect driver version, non-optimal or incorrect network configuration, wireless adapter settings, AP/router configuration, or interference issues.
How to fix it.
Follow the steps below to troubleshoot.
Click or the topic for details:
Driver
Is your driver up to date?
You don't need to update to the latest version unless you encounter issues. You can resolve many issues by updating an out-of-date driver.
To update the driver and software for your Intel® Wireless Adapter:
- Download the Intel® Driver & Support Assistant to automatically install the latest wireless driver and software.
- Or, manually identify your current driver version and download the latest driver.
For the driver updates on Intel® Killer™ products, visit this article
| Note | Your computer manufacturer might have customized drivers and software to enable or alter features, or provide improved operation on your computer. |
Wi-Fi Network
Is the Wi-Fi radio on?
If your computer doesn't see any Wi-Fi networks, verify if the Wi-Fi radio is on.
Select your operating system:
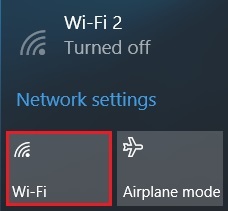
Windows® 10
Select the Network icon on the task tray at the bottom right of the screen. Click the Wi-Fi button to turn it on.
Windows 8.1*
Select the Network icon on the task tray at the bottom right of the screen. Click the slider under Wi-Fi to turn it on.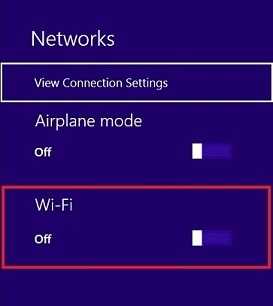
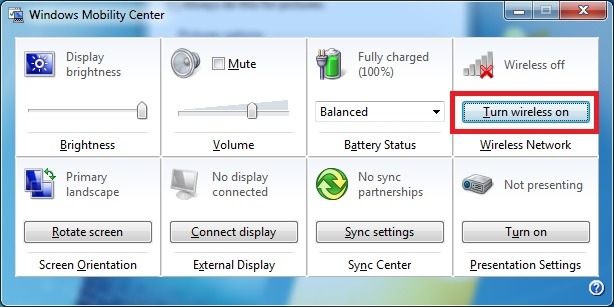
Windows 7*
Simultaneously press the Windows and X keys. Or, right-click the power icon in the task tray on the bottom right of the screen to launch the Windows Mobility Center.Select Turn wireless on if wireless is off.
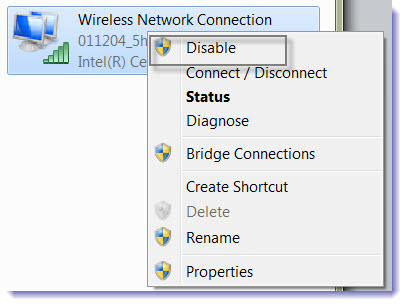
Is the Wi-Fi adapter enabled?
Go to Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network Connections, and right-click the adapter. If Disable is displayed as a configuration option, that means the adapter is enabled.
AP or Broadband Router
Is the wireless access point (AP) or Wi-Fi broadband router functioning?
Verify that your system can connect to your network and the Internet. You may use other Wi-Fi devices such as a smartphone or tablet to verify if the wireless AP or broadband router is functioning. Contact your access point vendor or Internet service provider for assistance.
Is the network adapter detected?
If you get an error message on start or at logon, see possible issues and regulatory requirements.
Interference
How do you check for sources of local interference?
Check for sources of interference, particularly if using IEEE* 802.11 Wi-Fi adapters working in the 2.4 GHz spectrum. Possible interference sources include:
- Cordless phones that operate in the 5 GHz spectrum
- Microwave ovens
- Bluetooth® technology-enabled devices
How do you identify interference or contention from other Wi-Fi networks?
Make sure the channel your access point or wireless router is using isn't overlapping or in use by another nearby access point.
- Software tools such as MetaGeek inSSIDer* help you select the best channel for your access point or wireless router.
- If using 2.4 GHz band, use only channels 1, 6, or 11.
- If using the 5 GHz band, use channels 36, 40, 44, or 48.
How do you disable automatic channel selection?
Some access points or wireless routers try to automatically select the best channel to use. The auto-selection can happen at startup or on-the-fly during normal operation. If you are experiencing random disconnects from the network, try the following:
- Disable the AUTO setting and manually select a channel.
- Software tools such as MetaGeek inSSIDer* help you select the best channel for your access point or wireless router.
- If using 2.4 GHz band, use only channels 1, 6 or 11.
Settings
How do you verify and adjust power management settings? How can those settings cause potential connection issues?
The power management or the Power Save Polling (PSP) setting lets you select a balance between power consumption and Wi-Fi adapter performance. See Setting Wireless Adapter Power Management to learn how to change the setting.
You may have connection issues with a Wi-Fi access point (AP) that doesn't support the PSP feature. See Power Save Polling Causes Connection Issues with Access Points for details.
| Note | Lowering the power management setting can cause the battery to discharge more rapidly when not connected to a power source. |
How do you check roaming settings?
Verify that the adapter property setting for roaming aggressiveness isn't at the minimum or the maximum. Learn how to configure the adapter settings.
What are the recommended 802.11n settings?
Review the recommended settings for 802.11n connectivity. These include using WPA2-AES security and 5 GHz. If you are using 2.4 GHz, we recommend narrow channels.
| Note | We recommend using channel bonding in the 5 GHz band. Channel bonding is helpful due to the limited available non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz band. |
What are the recommended 802.11ac settings?
Resetting Network Devices and Network Stack
Learn how to Reset Network Devices and Network Stack.
General recommendations
- If you are using Wi-Fi, minimize the number of solid objects between the access point’s antenna and the device suffering from low speeds, using line-of-sight. Moving a device or antenna even an inch to one side could bypass multiple solid objects, making an enormous difference
- Wi-Fi extenders have limited radio capacity, and will always provide at least slightly slower speeds than connecting directly to the router, as they have to use the same radio to receive and transmit, at the same time. If you are using Wi-Fi extenders, try the connection performance without them in testing purposes.
- If you are using a Wireless-N router in a crowded Wi-Fi environment, you are very likely to encounter drops and speed issues no matter what settings you change. Unfortunately, the 2.4 GHz spectrum is very limited on how many channels are available, and conflicts arise quickly. Updating to a Wireless-AC router may be required to increase your speeds and reduce wireless drops.
- If you are using an antivirus or firewall application, try completely uninstalling it for testing purposes. If you notice that your speeds increase dramatically with the antivirus or firewall application uninstalled, try installing a freshly downloaded version from the antivirus vendor official website. If that doesn’t help, then the issue may be one with the antivirus application itself. In that case, you will want to contact the support team for the antivirus application.
If you've tested all the troubleshooting suggestions above and still have the Wi-Fi Connection Issues, please contact your system manufacturer or click Contact support in the blue banner below to find the support options for your region. Be ready to explain the steps you tried.