Intel continues its multidecade journey to deliver technology at high standards of environmental responsibility.
Last April, Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger outlined Intel’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, both in our own operations and across our value chain. This included raising the bar on existing commitments and setting a goal to achieve net-zero Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions across our global operations by 2040.
Lowering greenhouse gas emissions is one of the semiconductor industry’s most complicated challenges due to the energy needed to make chips and the unique requirements of the manufacturing processes. This complexity is compounded as the semiconductor ecosystem must also expand globally to meet the growing demand for chips. Getting to net-zero requires identifying, developing and piloting novel green chemistry solutions, abatement tools, new equipment designs and facility systems, many of which do not exist today. As one of the world’s largest semiconductor companies doing research, design and manufacturing, Intel is deepening its long-standing collaboration across the ecosystem to achieve a future of more sustainable computing.
We are extending our sustainability efforts to drive three key focus areas to realize net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. First, we have a roadmap for reducing emissions across our manufacturing operations and office buildings. This includes investing in renewable electricity: As of the end of 2022, we exceeded 90% of our global renewable electricity usage1. Second, we’re collaborating with the industry and academia to develop semiconductor processing alternatives and energy efficiencies across the value chain and to establish standard reporting metrics. Third, we are increasing the energy efficiency and lowering the total carbon footprint of our products and platforms, which helps our customers achieve their sustainability goals. For instance, data center operators could see a 60% reduction in carbon dioxide emissions using 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors2.
Remaining focused and prioritizing these opportunities toward a common goal of net-zero greenhouse gas emissions is how we can help mitigate the impacts of climate change. I’m proud of the collaboration to date and to share details of the progress we’re making.
Reducing Emissions Across our Operations
We are continuing our investment in renewable electricity purchases and installations. In collaboration with local utility providers, Intel is creating new contracting mechanisms to facilitate the construction of utility-scale renewable electricity projects, like solar and wind, near many of our large sites across the world, as well as at new factory build-outs. On our campuses, we added 14 new solar installations, totaling 7 megawatts of generation capacity in the past three years. This brings our global portfolio of on-site solar installations to 30 megawatts. At the end of 2022, our global renewable electricity usage is approximately 91%, up from 80% in 20213. We are committed to finding credible and scalable renewable electricity opportunities to reach 100% globally by 2030.
To help reduce our overall impact on the environment, extend carbon footprint savings to our customers and lower our bottom line, we’re implementing energy-reduction and energy-efficiency measures throughout our operations. We have conserved 973 million kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy cumulatively since 20204 — the equivalent of more than 91,000 U.S. homes’ annual electricity use5 — with the help of efforts like HVAC cooling and compressed air efficiency. In 2022, we reduced our Scope 1 energy emissions by 6,000 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent with heat recovery measures and by streamlining our heating needs.
Looking ahead, we are investing in unique technologies to further reduce our footprint. This includes continuously advancing our systems to maximize the reuse of waste heat from our factories, thereby reducing our dependency on natural gas. We are also developing ultra-efficient abatement equipment, using the latest capabilities in artificial intelligence, software systems, and energy efficiency to create technologies that limit and potentially eliminate the use of fossil fuels for our future factory designs.
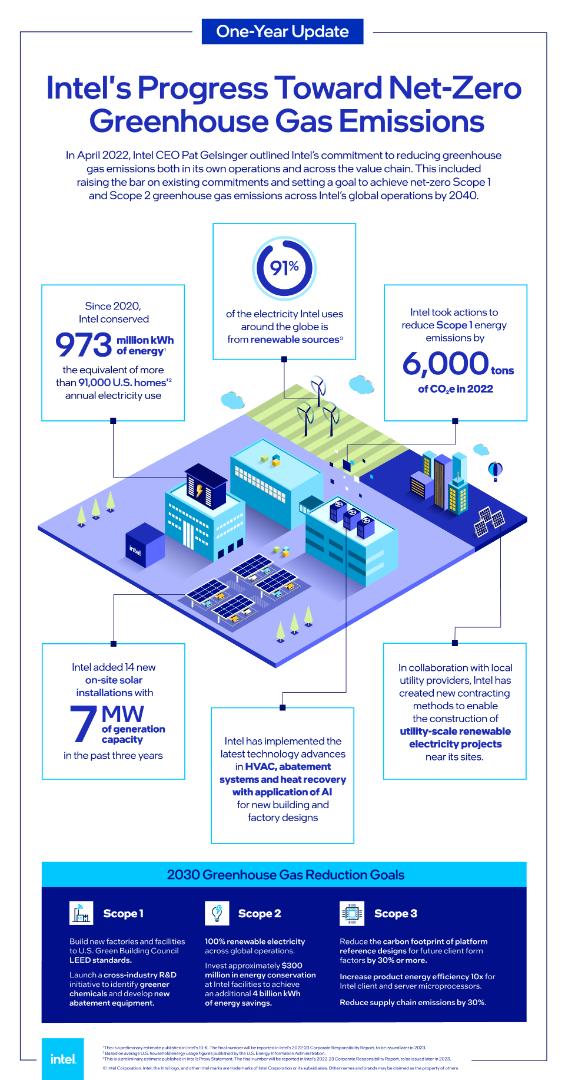
Collaborating Across our Value Chain
Intel is working with the industry association SEMI and the Semiconductor Research Corporation to set up a sustainable semiconductor manufacturing program that will strive to develop alternatives to various chemicals used in semiconductor manufacturing. In parallel, we are working with other leading industry partners to drive meaningful change within the ecosystem.
The newly created Semiconductor Climate Consortium (SCC), which brings together our suppliers, peers and customers, accelerates solutions that will reduce our industry’s greenhouse gas emissions. As a founding member, Intel helped spearhead the effort. Currently more than 70 companies across our value chain are participating.
We are also participating in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Product Attribute to Impact Algorithm (PAIA) consortium to develop a common approach to calculating product carbon footprint for electronics. This allows our industry to properly measure the progress we’re making and our customers to have a clearer understanding of their upstream emissions and embodied product carbon footprint.
And, together with Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany, Intel recently announced an academic research program in Europe that will leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to drive innovation in semiconductor manufacturing processes and technologies.
Increasing Power Efficiency of Intel Products and Platforms
New generations of Intel products are designed to deliver higher performance using less energy. Intel recently released our most sustainable data center processors, the 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. With built-in accelerators, these processors help improve performance per watt by an average of 2.9 times for select workloads6. Other features decrease energy consumption by up to 20% for targeted workloads with negligible impact on performance7.
To reduce e-waste, Intel is collaborating with the Open Compute Project (OCP) to advance modular designs to increase the reuse of server elements generation-over-generation.
Combined with our operational efforts, our holistic approach across products, platforms, software and solutions enables our customers to accelerate their sustainability journeys.
Committed to Net-Zero GHG Emissions
With leadership comes responsibility. A commitment to the environment and to reducing greenhouse gas emissions is not a nice-to-have, but a must-do. It is an opportunity to bring the entire value chain together, innovate and achieve our common goal. No company can do it alone.
Intel continues to be fully committed to the necessary actions, investments, innovations and collaboration to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions across our operations. I am pleased with the progress and look forward to more milestones to come.
Keyvan Esfarjani is executive vice president, chief global operations officer and general manager of Manufacturing, Supply Chain and Operations at Intel Corporation.
1This is a preliminary estimate published in Intel’s Proxy Statement. The final number will be reported in Intel’s 2022-23 Corporate Responsibility Report, to be issued later in 2023.
2Calculations as of March 28, 2023 based on the Intel® Node TCO & Power Calculator using default cost, power and TCO assumptions over a 5-year TCO horizon comparing replacing 50 older servers with Intel Xeon 4110 processors with new servers using new Intel Xeon 5420+ processors. Results may vary. Performance measurements based on published SPECrate®2017_int_base on spec.org as of March 28, 2023
3This is a preliminary estimate published in Intel’s Proxy Statement. The final number will be reported in Intel’s 2022-23 Corporate Responsibility Report, to be issued later in 2023.
4This is a preliminary estimate published in Intel’s 10-K. The final number will be reported in Intel’s 2022-23 Corporate Responsibility Report, to be issued later in 2023.
5Based on average U.S. household energy usage figures published by the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
6See intel.com/processorclaims: 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors. Claim E1. Results may vary.
7See intel.com/processorclaims: 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors. Claim E6. Results may vary.

