Visible to Intel only — GUID: svv1639406443200
Ixiasoft
1. About the Video and Vision Processing Suite
2. Getting Started with the Video and Vision Processing IPs
3. Video and Vision Processing IPs Functional Description
4. Video and Vision Processing IP Interfaces
5. Video and Vision Processing IP Registers
6. Video and Vision Processing IPs Software Programming Model
7. Protocol Converter Intel® FPGA IP
8. 3D LUT Intel® FPGA IP
9. AXI-Stream Broadcaster Intel® FPGA IP
10. Bits per Color Sample Adapter Intel FPGA IP
11. Chroma Key Intel® FPGA IP
12. Chroma Resampler Intel® FPGA IP
13. Clipper Intel® FPGA IP
14. Clocked Video Input Intel® FPGA IP
15. Clocked Video to Full-Raster Converter Intel® FPGA IP
16. Clocked Video Output Intel® FPGA IP
17. Color Space Converter Intel® FPGA IP
18. Deinterlacer Intel® FPGA IP
19. FIR Filter Intel® FPGA IP
20. Frame Cleaner Intel® FPGA IP
21. Full-Raster to Clocked Video Converter Intel® FPGA IP
22. Full-Raster to Streaming Converter Intel® FPGA IP
23. Genlock Controller Intel® FPGA IP
24. Generic Crosspoint Intel® FPGA IP
25. Genlock Signal Router Intel® FPGA IP
26. Guard Bands Intel® FPGA IP
27. Interlacer Intel® FPGA IP
28. Mixer Intel® FPGA IP
29. Pixels in Parallel Converter Intel® FPGA IP
30. Scaler Intel® FPGA IP
31. Stream Cleaner Intel® FPGA IP
32. Switch Intel® FPGA IP
33. Tone Mapping Operator Intel® FPGA IP
34. Test Pattern Generator Intel® FPGA IP
35. Video and Vision Monitor Intel FPGA IP
36. Video Frame Buffer Intel® FPGA IP
37. Video Frame Reader Intel FPGA IP
38. Video Frame Writer Intel FPGA IP
39. Video Streaming FIFO Intel® FPGA IP
40. Video Timing Generator Intel® FPGA IP
41. Warp Intel® FPGA IP
42. Design Security
43. Document Revision History for Video and Vision Processing Suite User Guide
23.4.1. Achieving Genlock Controller Free Running (for Initialization or from Lock to Reference Clock N)
23.4.2. Locking to Reference Clock N (from Genlock Controller IP free running)
23.4.3. Setting the VCXO hold over
23.4.4. Restarting the Genlock Controller IP
23.4.5. Locking to Reference Clock N New (from Locking to Reference Clock N Old)
23.4.6. Changing to Reference Clock or VCXO Base Frequencies (switch between p50 and p59.94 video formats and vice-versa)
23.4.7. Disturbing a Reference Clock (a cable pull)
Visible to Intel only — GUID: svv1639406443200
Ixiasoft
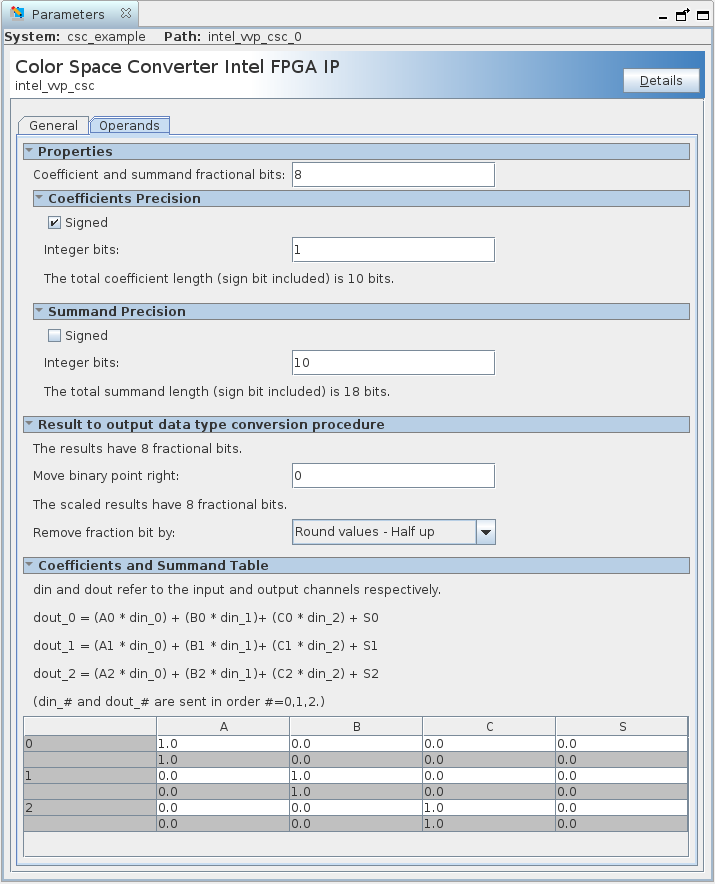
17.2. Color Space Converter IP Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Control Settings | ||
| Memory-mapped control interface | On or off | Turn on to specify Color Space Converter register values using the Avalon memory-mapped interface. |
| Separate clock for control interface | On or off | Turn on for a separate clock for the control interface. |
| Debug features | On or off | Turn on for debugging features (not applicable for lite mode). |
| Pipeline ready signals | On or off | Turn on to pipeline ready signals, which helps with improving Fmax. |
| Video Data Format | ||
| Lite mode | On or off | Turn on to operate the Color Space Converter in lite mode. |
| Input bits per color sample | 8 to 16 | Select the number of input bits per color sample. |
| Output bits per color sample | 8 to 16 | Select the number of output bits per color sample. |
| Number of pixels in parallel | 1 to 8 | Select the number of pixels in parallel. |
| Output Color space | RGB, YCbCr, or MONO | Only applies if Memory-mapped control interface and Lite mode are off. Use this to set the color space field value of outgoing image information packets. It does not affect the algorithmic values, only the metadata. |
| Parameter | Allowed range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Properties | ||
| Coefficient and summand fractional bits | 0 to 24 | Specify the number of fraction bits for the fixed-point type to store the coefficients and summands. |
| Coefficient precision: Signed | On or Off | Turn on to set the fixed-point type to store the constant coefficients as having a sign bit. |
| Coefficient precision: Integer bits | 0 to 16 | Specifies the number of integer bits for the fixed-point type to store the constant coefficients. |
| Summand precision: Signed | On or Off | Turn on to set the fixed-point type to store the constant summands as having a sign bit. |
| Summand precision: Integer bits | 0 to 20 | Specify the number of integer bits for the fixed-point type used to store the constant summands. |
| Result to output data type conversion | ||
| Move binary point right | -16 to +16 |
Specify the number of places by which to move the binary point to the right. Negative numbers indicate moving the binary point to the left. |
| Remove fraction bits by |
|
Select the method of discarding fraction bits resulting from the calculation. |
| Coefficients and Summand Table A0, B0, C0, S0 A1, B1, C1, S1 A2, B2, C2, S2 |
12 fixed-point values | Only when you turn off Memory-mapped control interface. Each coefficient or summand is represented by a white cell with a gray cell underneath. The value in the white cell is the desired value and is editable. The value in the gray cell is the actual value, determined by the fixed-point type specified. The gray cells are not editable. You can create a custom coefficient and summand set by specifying one fixed-point value for each entry. |
Figure 38. Color Space Converter General TabThe figure also shows the presets
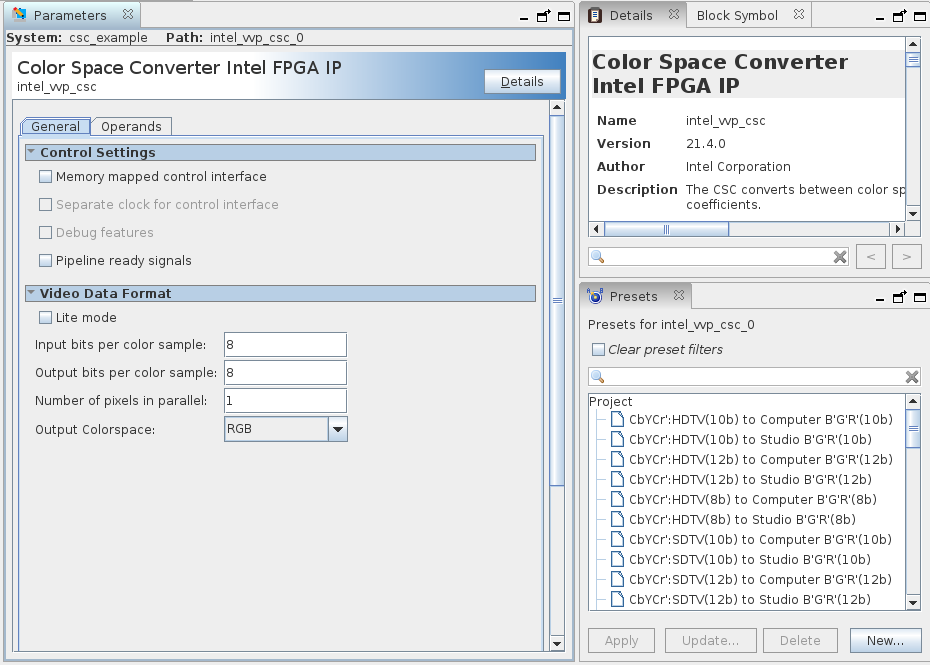

Figure 39. Color Space Converter GUI Operands Tab