Visible to Intel only — GUID: osa1651157203680
Ixiasoft
1. About the Video and Vision Processing Suite
2. Getting Started with the Video and Vision Processing IPs
3. Video and Vision Processing IPs Functional Description
4. Video and Vision Processing IP Interfaces
5. Video and Vision Processing IP Registers
6. Video and Vision Processing IPs Software Programming Model
7. Protocol Converter Intel® FPGA IP
8. 3D LUT Intel® FPGA IP
9. AXI-Stream Broadcaster Intel® FPGA IP
10. Chroma Key Intel® FPGA IP
11. Chroma Resampler Intel® FPGA IP
12. Clipper Intel® FPGA IP
13. Clocked Video Input Intel® FPGA IP
14. Clocked Video to Full-Raster Converter Intel® FPGA IP
15. Clocked Video Output Intel® FPGA IP
16. Color Space Converter Intel® FPGA IP
17. Deinterlacer Intel® FPGA IP
18. FIR Filter Intel® FPGA IP
19. Frame Cleaner Intel® FPGA IP
20. Full-Raster to Clocked Video Converter Intel® FPGA IP
21. Full-Raster to Streaming Converter Intel® FPGA IP
22. Genlock Controller Intel® FPGA IP
23. Generic Crosspoint Intel® FPGA IP
24. Genlock Signal Router Intel® FPGA IP
25. Guard Bands Intel® FPGA IP
26. Interlacer Intel® FPGA IP
27. Mixer Intel® FPGA IP
28. Pixels in Parallel Converter Intel® FPGA IP
29. Scaler Intel® FPGA IP
30. Stream Cleaner Intel® FPGA IP
31. Switch Intel® FPGA IP
32. Tone Mapping Operator Intel® FPGA IP
33. Test Pattern Generator Intel® FPGA IP
34. Video Frame Buffer Intel® FPGA IP
35. Video Streaming FIFO Intel® FPGA IP
36. Video Timing Generator Intel® FPGA IP
37. Warp Intel® FPGA IP
38. Design Security
39. Document Revision History for Video and Vision Processing Suite User Guide
22.4.1. Achieving Genlock Controller Free Running (for Initialization or from Lock to Reference Clock N)
22.4.2. Locking to Reference Clock N (from Genlock Controller IP free running)
22.4.3. Setting the VCXO hold over
22.4.4. Restarting the Genlock Controller IP
22.4.5. Locking to Reference Clock N New (from Locking to Reference Clock N Old)
22.4.6. Changing to Reference Clock or VCXO Base Frequencies (switch between p50 and p59.94 video formats and vice-versa)
22.4.7. Disturbing a Reference Clock (a cable pull)
Visible to Intel only — GUID: osa1651157203680
Ixiasoft
17.2. Deinterlacer Parameters
The IP offers run- and compile-time parameters.
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Video Data Format | ||
| Bits per color sample | 8 to 16 | Select the number of bits per color sample. |
| Number of color planes | 1 to 4 | Select the number of color planes per pixel. |
| Number of pixels in parallel | 1 to 8 | Select the number of pixels in parallel. |
| Control | ||
| Lite mode | On or off | Turn on to operate the bob deinterlacer in lite mode. |
| Memory-mapped control interface | On or off | Turn on to read frame statistics and turn the bob deinterlacer on and off using an Avalon memory-mapped interface. The memory-mapped control interface is mandatory in lite mode. |
| Separate clock for control interface | On or off | Turn on for a separate clock for the control interface. |
| Deinterlacer Behavior | ||
| Bob deinterlacing mode | DEINTERLACE_F0_ONLY, DEINTERLACE_F1_ONLY, DEINTERLACE_F0_AND_F1 |
Select to drop of F0 or F1 input fields. |
| Maximum Frame Size | ||
| Maximum field width | 32 to 16384 | Select the maximum field width to determine the size of the line buffer. Set this parameter to the line length of the widest fields you want to deinterlace. Progressive frames of any size pass through unchanged. |
| General | ||
| Debug features | On or off | Turn on to enable debug features (not applicable for lite mode). |
Figure 40. Deinterlacer GUI
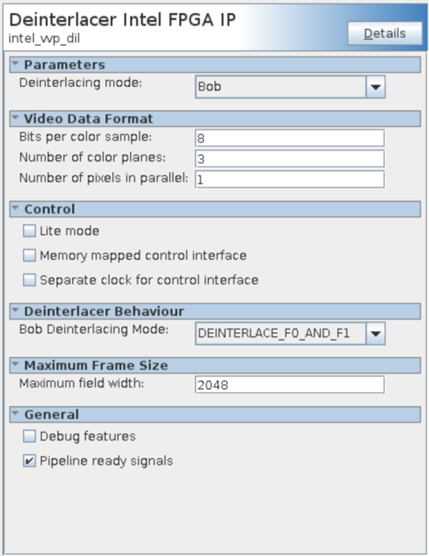

Figure 41. Bob Deinterlacing ModeThe figure shows the bob deinterlacing modes where the IP drops or deinterlaces interlaced fields. The IP passes all progressive frames through.