Using Celadon in Virtual Machine to Build Innovative Android Solutions on x86
Target Customers
Vendors seeking to build or upgrade existing devices for a Retail Point-of-Sale to perform smart and fast transactions.
Introduction
In the retail market segment today, most of the larger retail enterprises have adopted integrated fixed/mobile POS devices but over 50% of the retailers still do not use a POS device. Rather, they are using a combination of manual methods, cash registers, QuickBooks for bookkeeping. However, with the evolution of cashless transactions and advanced analytics to determine inventory records, customer management, and employee management, the demand for robust and smarter POS solutions is increasing considerably. The global POS software market was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2019 and is projected to expand at a CAGR of 10.1% over the forecast period of 2020-2027 (Grand View Research, 2020 “Point of Sale Software market size report”). These devices are highly versatile and can be expanded to other systems like kiosks, video surveillance, mobile POS which is driving the demand for point of sale software.
Retail stores can be digitized with Smart payment, contactless transactions, reduce the wait time by fast billing, quick scan of the QR codes, promotional content display etc. This solution brief focusses on the POS edge-based solution for Retail segment using Celadon in a Virtual machine as edge computing software on Intel X86 platforms. The power of X86 architecture ensures fast and robust transactions along with Android OS offering a better user experience and richer capabilities with its software.
This solution can further be extended for richer use cases like inventory management, personalized promotion content display as well as offers new services (Labor automation, Theft management) using AI capabilities on X86.
For the existing POS customer devices running on Windows or Linux OS, this solution also provides the flexibility to run Celadon in VM in parallel with other OSes to help vendors cater to many customers without any software compatibility issues on Intel x86 platforms
Celadon based POS solutions improve performance and reduce software compatibility issues for retailers.

Smart POS Use Case
Figure 1 depicts the overall use case of a POS device in the retail space.
The POS device is running Celadon in VM over Ubuntu on X86 HW running retail use cases using Android Applications.
The POS device uses the Android Applications to enable use cases like smart payment transactions in moving toward cashless transactions, quick scan of the merchandise with integrated cameras scanners in reducing the wait time, share transaction details to the customer via external display for accuracy, display of promotional content to external displays, self-checkout capabilities in enabling contact less transactions.
Customers can experience Quick transactions due to the multi-core x86 capabilities in enhancing the overall customer experience in Retail stores.
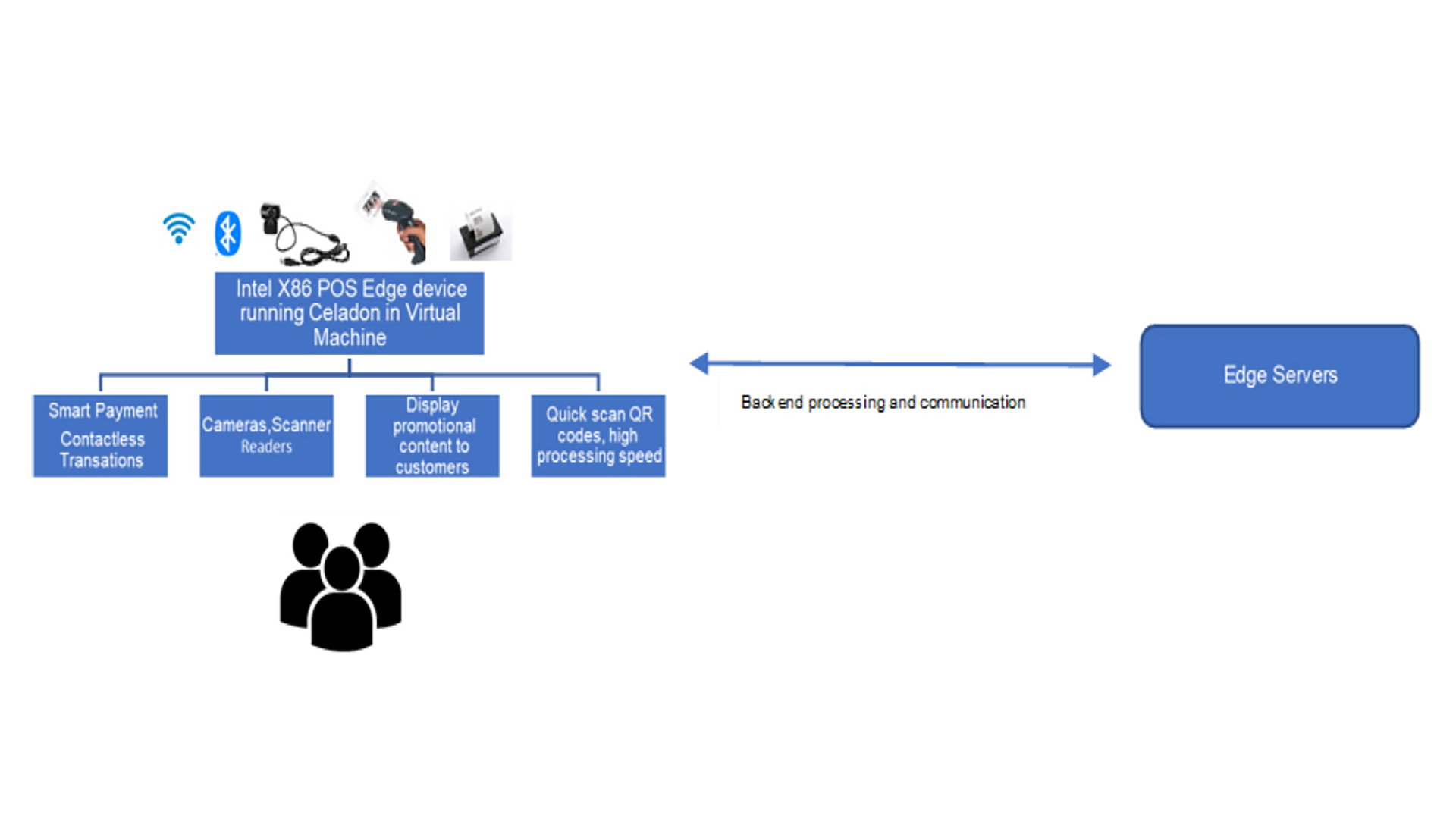
Figure 1. Point of Sale device is a critical element of all retail workflows
Software Stack for Point of Sale System
Figure 2 below describes the Celadon in Virtual Machine software stack that works seamlessly on x86 devices. The POS device runs on Android software stack in a virtual environment over KVM hypervisor. The image is launched over the Ubuntu* host operating system.
The KVM/QEMU is configured to provide a modern, virtual hardware platform, that maximizes the abstraction of the physical hardware platforms. This advanced virtualization technology also leverages Intel’s IP capabilities, such as Intel® Graphics Virtualization Technology (Intel® GVT), single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV), Trusted Platform Module (TPM), and more. The key component that makes Celadon unique, however, is the auto adaptation framework (AAF). AAF automatically detects and binds system kernel drivers and loads the hardware abstraction layer (HAL) modules and configurations for a variety of devices exposed on Intel platforms. This means that each application is served by a single Celadon image with a unified architecture, allowing for the consolidation of many workloads onto a single device.
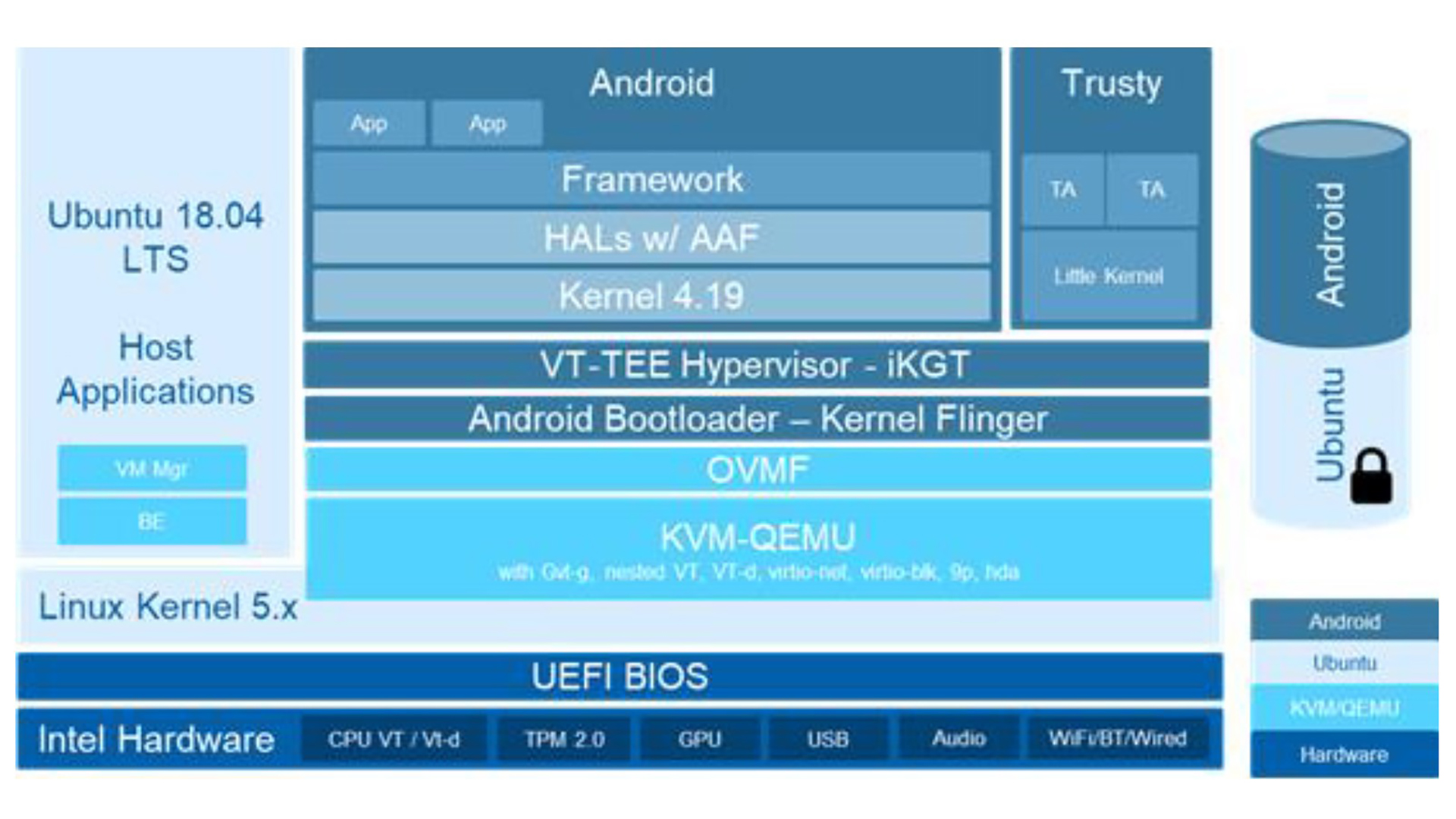
Figure 2. Celadon in Virtual Machine architecture
Key Android Capabilities for POS Use Cases:
- Multi-display, multi-camera support
- USB device management, USB audio capabilities
- Secure guest-OS, host OS hardening, TPM 2.0
- Integrated sensor hub for sensor management
- Power management through Android
- Thermal management through Android
- Connectivity - WiFi, Bluetooth, Ethernet control through Android
Android SW capabilities processed with a powerful Intel x86 CPU and GPU is an Ideal solution for a high-performance retail solution like POS. This can be further expanded to perform artificial intelligence use cases for retail store automation and management using the Google Android NN API capabilities integrated with the OpenVINO™ framework powered by VPU accelerators such as Intel® Movidius™ Myriad™.
Conclusion - Key Solution Benefits
POS devices are a key growth area in the retail segment today with opportunities to improve customer experience, reduce cost and increase profitability, and facilitate business growth.
For enterprises with requirements of high performance, high security, and a low-latency edge computing solution, Celadon in VM (CiV) running on Intel x86 is the ideal choice.
Benefits can be seen across the product value chain, including:
- Accelerated development. CiV offers tools and sample code for a secure platform that includes a framework on which it is easy to develop and debug.
- Improved efficiency. Vendors can build innovative and smart fixed or mobile POS products on optimized Intel architectures, leveraging powerful CPU and GPU capabilities.
- Operating system flexibility. Platform support for both Windows and Android on a single hardware platform allows end users to take full advantage of both software ecosystems.
- Expandability. Customers can re-use the product ecosystem by expanding the automation via VPU/AI capabilities