Introduction
This guide is targeted towards users who are already familiar with Microsoft* SQL Server* and provides pointers and system settings for hardware and software that will provide the best performance for most situations. However, please note that we rely on the users to carefully consider these settings for their specific scenarios, since Microsoft SQL Server can be deployed in multiple ways, and this is a reference to one such use-case.
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. SQL Server is offered in many different editions, but this guide will focus on the SQL Server Enterprise edition. SQL Server’s database architecture is based on a Client-Server architecture model. This tuning guide will focus on Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads (TPCE like) while using SQL Server for Windows*.
4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors deliver industry-leading, workload-optimized platforms with built-in AI acceleration, providing a seamless performance foundation to help speed data’s transformative impact, from the multi-cloud to the intelligent edge and back. Improvements of particular interest to this workload applications are:
- Enhanced Performance
- More Intel® Ultra Path Interconnect (Intel® UPI)
- Increased DDR5 Memory Speed & Capacity
The hardware and software used in testing the server configuration for this tuning guide:
| Hardware | Memory | 32 * 64GB Hynix DDR5, 4400MT/s |
| I/O Controllers | 4x RS3SC008 Intel Raid | |
| Disks | 1 x Intel® 1.9TB SSD OS Drive 10 x Intel® SC2KG019T7 SSD (1.9TB) Backups 8 x Intel® SC2KG960G8 SSD (960GB) Log 5 x Intel® SC2BA800G3 SSD (800GB) Tempdb 2 x Intel® SC2BB016T4 SSD (1.6TB) mdf 85 x Intel® SC2KG960G8 SSD (960GB) DB |
|
| NIC | 2x Intel® Ethernet Network Adapter X520 Series 210G BASE-T | |
| Software | Operating System | Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Datacenter |
| Kernel | 10.0.20348 Build 20348 | |
| SQL Version | 2022.160.1000.6 | |
| Workload Kit | TPCE Kit 1041 | |
| Benchcraft | 2.5.6 |
Note The configuration described in this article is based on 4th Generation Intel Xeon processor hardware. Server platform, memory, hard drives, network interface cards can be determined according to customer usage requirements.
Hardware
BIOS
Please note, that all BIOS settings outlined below are based on Intel’s Software Development Platforms designed for the 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. Begin by resetting your BIOS to default setting, then follow the suggestion below for changes:
| Configuration Item | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration -> Hardware Prefetcher | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration -> Adjacent Cache Prefetch | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration -> DCU Streamer Prefetcher | Enabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration -> DCU IP Prefetcher | Enabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration -> LLC Prefetch | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU P State Control -> Energy Efficient Turbo | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU P State Control -> Turbo Mode | Enabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> UP Configuration -> UPI General Configuration -> Boot Performance Mode | Max perf |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> Hardware PM State Control -> Hardware P State | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU - Advanced PM Tuning -> Energy Perf BIAS -> ENERGY_PERF_BIAS_CFG_mode | Performance |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU - Advanced PM Tuning -> Energy Perf BIAS -> Workload Configuraiton | I /O sensitive |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Memory Configuration -> Memory RAS Configuration -> Patrol Scrub | Disabled |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU C State Control -> Package C State | Co\C1 state |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU C State Control -> Enhanced Halt State (C1E) | Disable |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU C State Control -> CPU C6 Report | Disable |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU C State Control ->CPU C1 auto demotion | Disable |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Advanced Power Management Configuration -> CPU C State Control -> CPU C1 auto undemotion | Disable |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Common RefCode Configuration -> UMA-Based Clustering | Disable (All2All) |
| EDKII Menu -> Socket Configuration -> Uncore Configuration -> Uncore General Configuration -> SNC (Sub NUMA) | Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) |
Memory Configuration
This workload runs best with 2 DIMMS per channel populated with 4400 MTS DDR5 registered memory. For specifics consult your platform’s manual.
Storage
The table below details the type and number of drives used. Each type of drive sets (DB, Temp DB, etc.…) are organized into RAID volumes, with the DB drives being evenly split into RAID0 volumes per IO controller. The only exception to this is the LOG volume which is configured as RAID10. The following are the recommended settings for the RAID volumes and can be set via the Intel® RAID Web Console 3 for Windows.
| Drive Purpose | RAID Level | Stripe Size (KB) | Read Ahead | Write Back Cache Policy | Disk Cache Policy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB | 0 | 64 | No | Write Through | Enabled |
| Temp DB | 0 | 64 | No | Write Through | Enabled |
| Backups | 0 | 64 | Yes | Write Through | Enabled |
| Log | 10 | 64 | No | Write Back | Enabled |
Network
This workload runs best with the following settings for all adapters connecting the Server to the Client:
The following PowerShell script is used as an example with ‘Ethernet 2’(say):
Set-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name "Ethernet 2" -RegistryKeyword '*JumboPacket' – RegistryValue '9014' Set-NetAdapterRss -Name "Ethernet 2" -Enable 1 -BaseProcessorGroup 0 -BaseProcessorNumber 0 -MaxProcessors 16 -NumaNode 65535 -MaxProcessorGroup 0 -MaxProcessorNumber 16 -NumberOfReceiveQueues 8 -Profile Closest
In addition, the following must be set in SQL Server using the SQL Server sp_configure command.
sp_configure network_packet_size,8192 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE Go
Software Tuning
Software configuration tuning is essential. From the Operating System to SQL Server configuration settings, they are all designed for general purpose applications and default settings are almost never tuned for best performance.
Microsoft Windows Server* 2022 settings
| Configuration Item | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Windows Firewall | Control Panel -> Windows Firewall -> Tunr Windows Firewall on or off (left side of panel) -> select Turn Off Windows Firewall for both private and public networks |
| Visual Performance Setting | Computer -> properties -> advanced system settings -> advanced -> performance -> settings -> visual: adjust best performance |
| Virtual Memory Setting | Computer -> properties -> Advanced tab, virtual memory: change custom size: 4096 intial and maximum (not system managed) |
| Power Profile | Control Panel -> Hardware and Sound -> Power Options -> High Performance Option |
| Large Page Enable | Large Page Enable (Reboot to take effect): Control Panel -> Administrative tools -> local security policy -> local policy -> user rights assignment -> Lock pages in memory -> properties -> add user or group -> Administrators (or the user to be used with SQL Server) |
| Remove Windows Defender | PowerShell command: Remove-WindowsFeature - Name Windows-Defender-Features |
OLTP Architecture
The TPC-E like workload consists of transactions that simulate the interchanges commonly associated with brokers, customers, and a real-time stock exchange. These transactions are intended to represent a balanced mixture of disk input/output and CPU usage. Performance is measured in transactions per second and reported as tpsE.
Example of an OLTP benchmarking hardware configuration:
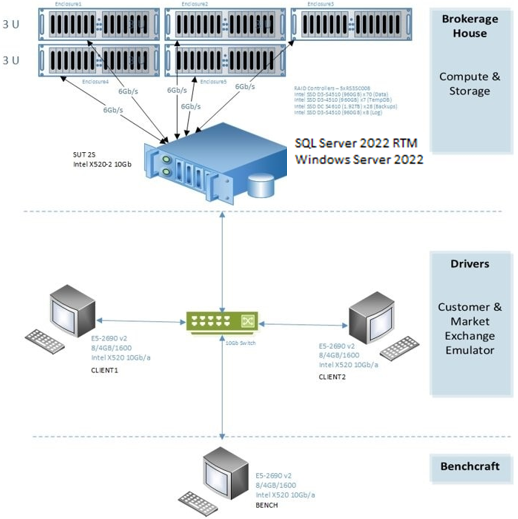
Tuning SQL Server for OLTP Workload
The following sp_configure commands should be used to configure SQL Server:
sp_configure show_advanced_options,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure backup_compression,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure "default trace enabled",0 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure lightweight_pooling,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure max_degree_of_parallelism,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure max_serv,<This number should be equal to 90% of system memory> go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure max_worker_threads,3000 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure priority_boost,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure recovery_interval,32767 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure remote_query_timeout,0 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure set_working_set_size,1 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go sp_configure network_packet_size,8192 go RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE go
The following flags should be used on the command line when starting up SQL Server prior to running the OLTP workload.
Sqlservr.exe -x -c -T827 -T652 -T661 -T834 -T3502 -T3979 -T8040 -T8095 -T8099 -T8088 -T8744 -T9038 -T8101
Related Tools
Microsoft Windows Performance Monitor tool (Perfmon) can be used to monitor overall system and disk performance metrics.
Best Practices for Testing and Verification
This workload is best run just after a fresh restoration of the database from backup and restart of the system. This workload should drive CPU Utilization to 99% across all logical processors. CPU kernel utilization should be around 12%. This is an I/O intensive workload that is characterized by approximate 850K IOPs, Random Access, and a 90/10 Read/Write ratio. The clients for this workload initiate transactions with 500+ simultaneous connections to the system under test with 500+ transactions in flight. This workload is more sensitive to memory speed than capacity. Typically, this workload reaches peak performance with memory size equal to about 3% of the database size. For verification of the database integrity, refer to the TPCE kit mentioned in resources for details. The TPCE kit provides verification tools suitable for an audit per the TPCE benchmark spec.
Conclusion
We have shared our best-known methods to optimally benchmark our 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors using an OLTP benchmark. We have covered both software and hardware configuration considerations to get the best performance.
Additional Resources
Transaction Processing Council
TPCE benchmark kit version 1.14.0