How many security camera feeds can a single person monitor effectively? Even assuming one person can handle all camera feeds for an entire facility, how many people are needed for 24/7 monitoring of twenty different sites, each in a different state or country? Now let’s give this task to a computer that can simultaneously monitor every single camera feed for all facilities without needing to take a break or even blink.
This is a real AI application, possible thanks to advancements in computer vision.
Computer Vision: Part of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Family
Computer vision acts as the eyes of artificial intelligence (AI), teaching computers to see and understand visual input, such as digital images and videos. Computer vision AI models coupled with additional downstream processes can then react to what the computer sees with actions or judgment. Computer vision not only enables AI applications to closely and accurately observe three-dimensional space, but to also inhabit and navigate that space to streamline monotonous work.
Main computer vision tasks include:
- Image recognition
- Image classification
- Image segmentation
- Object detection
- Object tracking
- Anomaly detection
- Anomaly segmentation
- Content-based image retrieval
Once one or more of these tasks are successfully performed, computer vision solutions can then perform a function. This automated action can range from monitoring available spots in a parking lot to identifying faults in a production line to helping researchers count animal or insect populations.
In this article, we’ll look at some of the most exciting computer vision applications in the following industries:
- Industrial automation and manufacturing
- Quality control
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- Scientific research
- Retail
- Video security and safety
- Smart cities
Computer Vision Applications in Different Industries
Computer vision AI has advanced leaps and bounds from the first experiments in which it was trained to sort circles and squares in the 1950s. Today, you can find organizations and individuals using computer vision daily—in hospitals, farms, warehouses, and on smartphones.
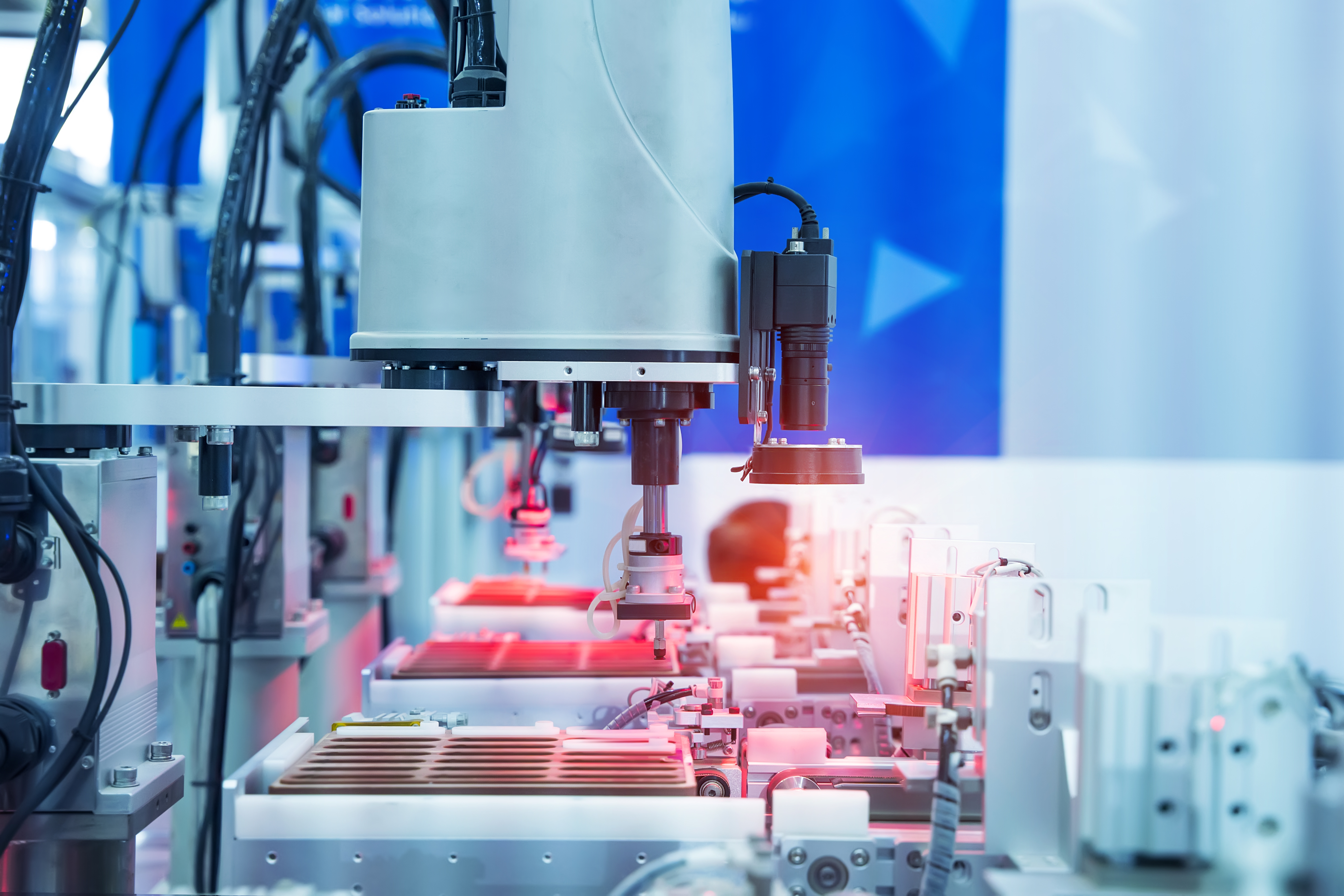

Manufacturing Applications
Computer vision applications in manufacturing enable automation, allowing manufacturers to produce quickly and efficiently while reducing human intervention and error.
Automated product assembly. Computer vision’s ability to guide the assembly process ensures quick and efficient production. Equipped with such capabilities, computers can visually monitor every step of assembly, potentially leading to more accurate manufacturing and helping detect production line errors, such as when parts are fitted incorrectly or products are packaged with problems.
Predictive and preventive maintenance. A monitoring system equipped with computer vision AI can visually analyze equipment for signs of wear and tear and alert maintenance. Manufacturing plants can keep small maintenance problems from becoming larger and more expensive (preventive maintenance), or keep failures from occurring at all (predictive maintenance).
Remote visual monitoring and automated responses. Many nooks and crannies of a manufacturing plant are not easily monitored manually. Computer vision helps plants monitor out-of-the-way equipment remotely and automate processes to mitigate specific problems that may arise, while helping keep workers safe.
Inventory management. Through video monitoring, computer vision enabled machines can recognize different parts and supplies, evaluate their quantities, and keep track of what needs to be replenished. Companies gain visibility of their inventory and workers are freed up from repetitive and automatable inventory management tasks.

Quality Control Applications
Quality control is crucial, whether you’re talking about healthcare, industrial manufacturing, or food production. Whenever quality dips, customer satisfaction drops, costs go up, production stalls, the supply chain fails, and in the worst cases, people may get hurt.
Defect detection. AI models can be trained to identify defects, including problems in production or damages to equipment, through real-time object detection. As far as the benefits of computer vision defect detection, AI can be much more accurate and faster than manual inspection. With input coming from regular camera surveillance and processing occurring centrally, defect detection is easily scaled to multiple facilities and locations.
When Intel applied computer vision AI to defect detection in tire manufacturing, accuracy was increased to 99.9%, cutting labor costs by USD 42,000. When used to inspect contact lenses, inspections were carried out 50 times faster than before, with 3 times the accuracy.
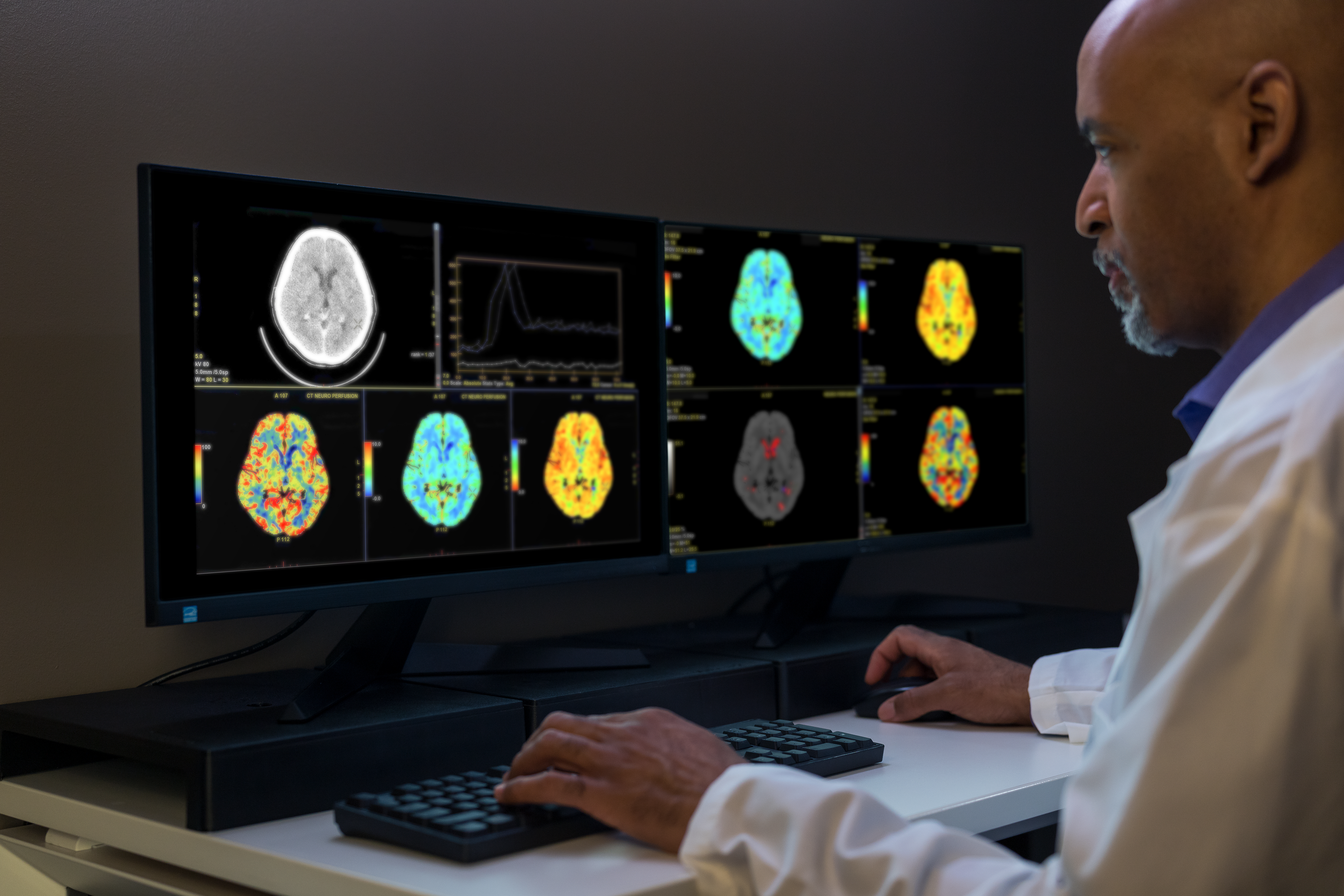
Healthcare Applications
When lives are at stake, processes and information must be as precise as possible. With its quick computing capabilities, artificial intelligence can assist medical personnel.
Medical image enhancement & analysis. Medical diagnostics depend on the careful study of images and scans. However, medical imaging data analysis takes precious time and attention. That’s where computer vision steps in. Properly trained AI algorithms can rapidly process and analyze large volumes of ultrasound images, CT scans, MRI scans, and X-ray images to assist and streamline clinician workflows.
Remote patient monitoring. While vital signs can easily be monitored remotely, there are other factors that computers would not normally observe but are key for tracking patients. For example, unsteady walking or irregular body posing could indicate an impending fall or injury. With computer vision, these activities can be monitored remotely and can be integrated to trigger further action, such as notifying nurses, for a more holistic patient care.
Disease progression screening. There are many examples of how computer vision can contribute to disease progression screening through image recognition, classification, and segmentation. For instance, as cameras observe waiting rooms or emergency departments, they can identify rapid respiration, which could indicate potential respiratory illness.

Agriculture Applications
Agriculture is not often the first industry people think of when it comes to leading-edge technology. However, agriculture and farming have been advancing in leaps and bounds as tech like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence become more accessible.
Crop health monitoring. Computer vision makes it possible to catch crop stress early and proactively treat the problem. Companies can train AI models to recognize different kinds of plant diseases, such as wheat rust, an infestation of insects, pests or fungus, malnutrition, nutrient deficiency, or dehydration. Based on the analysis of this data, they can take appropriate action to deal with and rectify these issues.
Automatic spraying, weeding, fertilizing, and irrigation. Once pests or weeds are identified by the trained AI model, robots (or workers) can be deployed for targeted pesticide treatment and weed removal, saving nearby healthy plants from being affected and reducing the amount of pesticides and herbicides put into the environment.
Crop stage monitoring. Smart agriculture solutions using computer vision can identify different crop stages, such as the precise time to begin harvesting or when plants are flowering and in need of heading. It can even estimate yield prior to harvest.
Automatic harvesting. Until recently, harvesting most crops has been a strictly manual process, as machines weren’t smart enough to identify ripe plants or gentle enough to harvest without damaging the crops. With advances in both computer vision and picking robots, it is now possible to automate harvesting and complete the cycle of autonomous farming.
Scientific Research and Computer Vision
Not all computer vision advancement happens in the field. In fact, many of the use-cases out there were crafted by scientific researchers.
Animal recognition and monitoring. Researchers have found success training AI models to recognize specific animals through recognition of both faces and hide patterns. Once individual animals can be identified, they can be monitored. General functions, such as animal counting or location tracking, are enhanced, while specific operations such as remote food and water intake monitoring, heat detection, weight measurement, and behavioral patterns are made possible.

Retail Applications
Online shopping has not been kind to in-store retail. Luckily, technology like artificial intelligence and computer vision help retailers improve user experience, avoid theft and loss, and manage many other critical aspects of retail.
Touchless and cashierless check out. Computer vision, combined with other sensors, detects product prices, calculates the total bill, and automatically charges customers. Computer vision helps cashier-less stores make sure their customers pay for everything that walks out of the store, such as with Amazon Go and its Just Walk Out technology.
Stock management. Computer vision AI models can analyze data from cameras scanning shelves every few seconds or through a video feed, notifying staff when stock needs to be replenished.
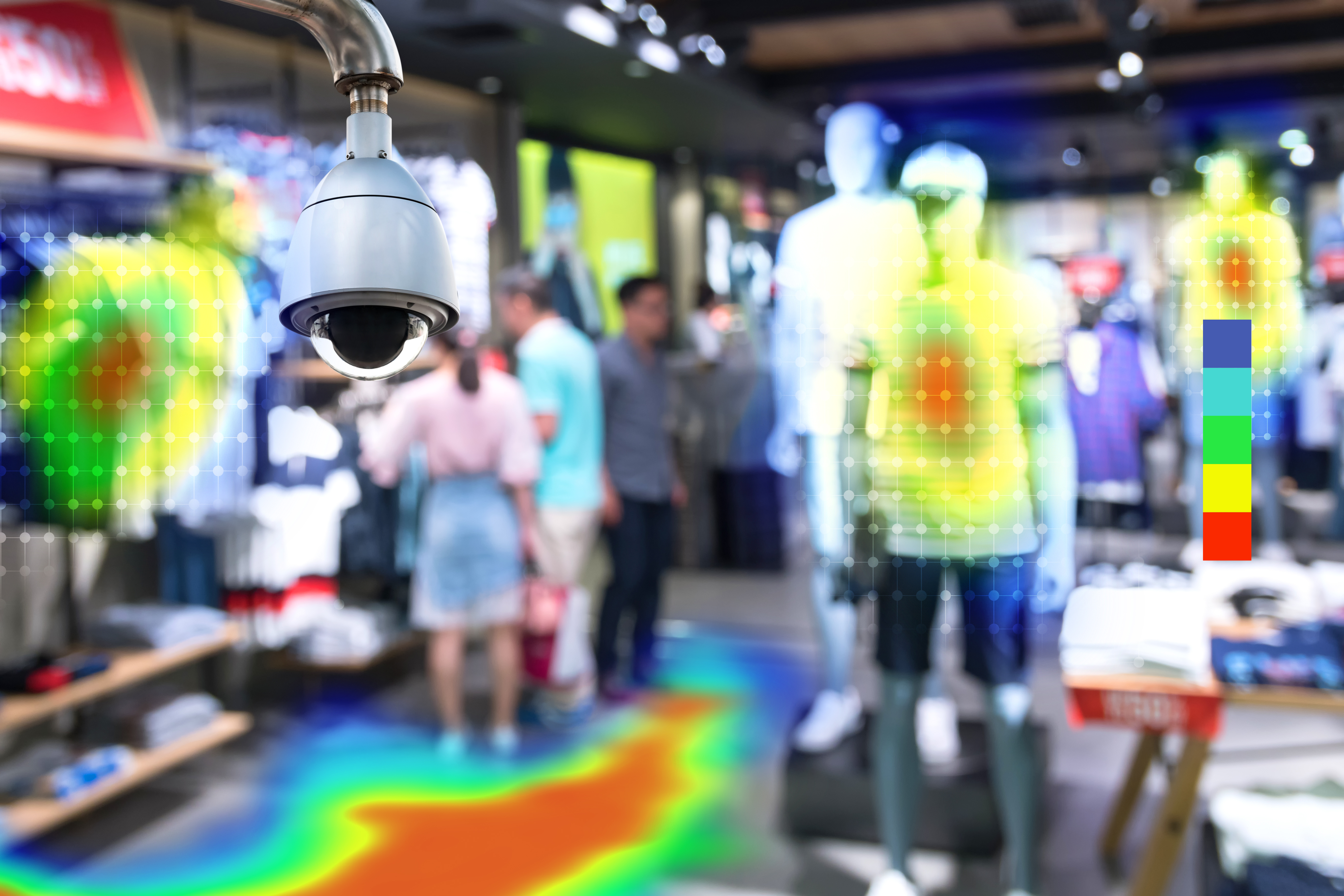
Customer behavior tracking. Using computer vision to count people helps retailers track how many people enter and leave a store. Additionally, traffic heat maps provide valuable data for optimizing store layout to improve flow. Facial recognition can also tell retailers which products and locations are most eye-catching. This computer vision application was especially beneficial for managing traffic during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Security Applications
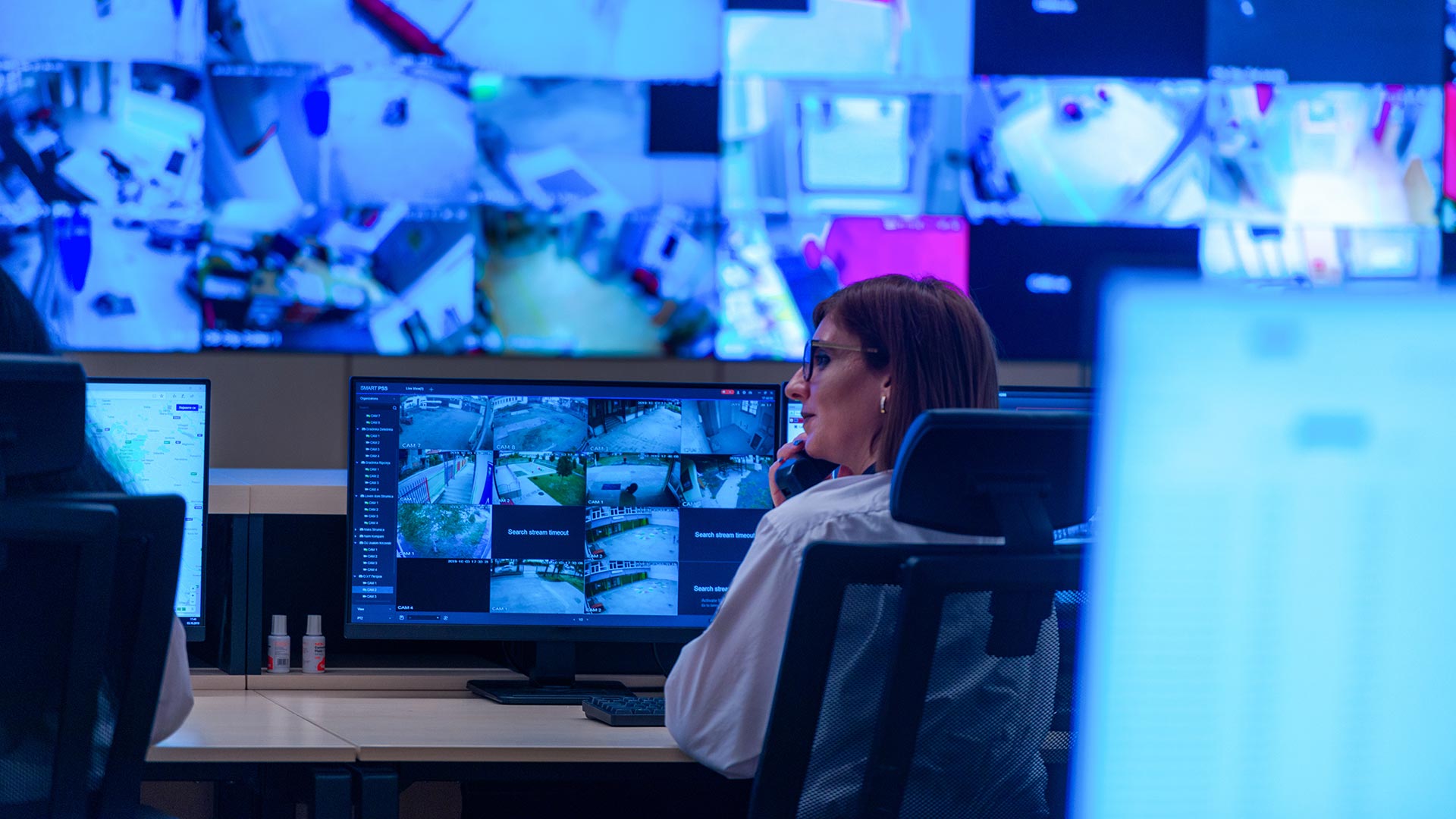
Video surveillance can become extremely accurate and effective when observed by computer vision AI models. Not only can AI process image input very fast, but it can do so for any number of camera feeds in any number of locations simultaneously.
PPE-Use monitoring. Whether looking for reflective vests and helmets at manufacturing plants or mask use in commercial establishments, personal protective equipment is necessary to keep people safe. Alerts are then triggered when PPE is missing or misused, preventing injury or safety violations.
Social distance monitoring. Cameras capture high-density areas, and purposely trained computer vision models can analyze such feeds to estimate the space between individuals, marking those too close to each other.

Smart City Applications
As the global population races towards 8 billion, more and more people crowd the world’s metropolitan areas. Smart city solutions help improve safety, mobility, and quality of life in an increasingly overpopulated society. While many of the previous computer vision AI applications fit into a smart city, here are a few noteworthy initiatives.
Autonomous traffic management. Traffic congestion is becoming an ever-present problem as the population rises. Computer vision enables governments to analyze traffic flow in a non-invasive way and optimize stoplights and street signage accordingly–or even notify emergency services in case of a traffic accident.
Infrastructure management. Data scientists can train computer vision algorithms to recognize road and bridge problems, such as potholes and cracks. When accessing data from cameras attached to delivery vehicles, for example, AI can analyze virtually every road and bridge in an entire county, informing road and bridge maintenance.
Emergency prediction and response. When regular surveillance feed is combined with satellite imagery and computer vision, natural disasters can be caught early in order to take necessary precautions.
A Constantly Evolving Field
On the conservative side, computer vision can improve accuracy and speed for a range of different tasks and applications. It can allow organizations to improve quality, efficiency, and costs. The potential of computer vision AI doesn’t stop there.
The new Intel Geti software enables a seamless experience allowing users to label, train, and optimize AI models for computer vision applications.